Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Calculating Kinetic Energy Lab
Calculating Kinetic Energy Lab. As might be implied by the above equation, 1 joule is equivalent to 1 kg* (m/s)^2. Kinetic energy depends on the velocity of the object squared.
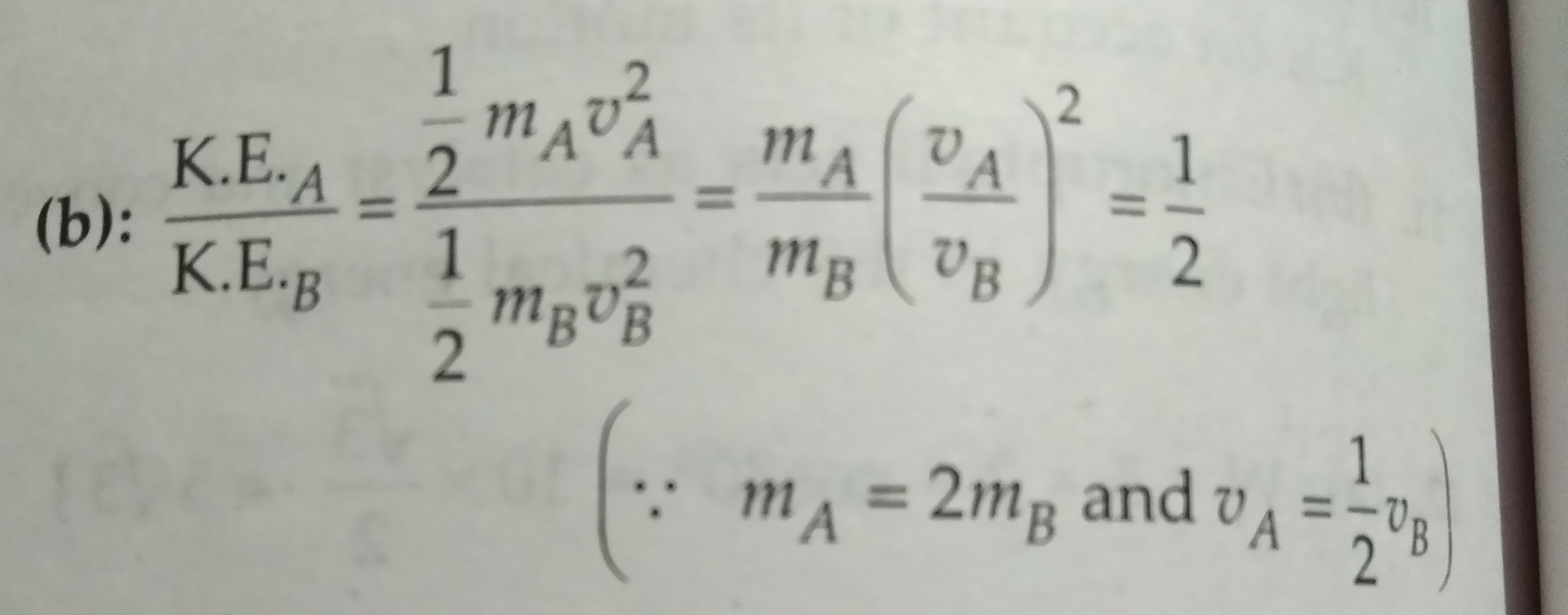
In this lab, the letter “ k ” is used to represent the kinetic energy, and “ v2 ” is used to represent the velocity squared. In classical mechanics, kinetic energy (ke) is equal to half of an object's mass (1/2*m) multiplied by the velocity squared. This lab uses vegetable racers that the students construct and race down a ramp to allow calculation of kinetic energy.
Put Those Values In The Above Formula.
The activation energy of a reaction is determined by graphical means using experimental data. What i want to find. Kinetic energy depends on the velocity of the object squared.
Calculate The Mass Of The Object Moving At A Speed Of 40 M/S And Having A Kinetic Energy Of 1500 J.
As might be implied by the above equation, 1 joule is equivalent to 1 kg* (m/s)^2. ∴ kinetic energy is 11,250 j. Kinetic energy of the objects having mass m and velocity v can be calculated with the formula given below;
Unlike Velocity, Acceleration, Force, And Momentum, The Kinetic Energy Of An Object Is Completely Described By Magnitude Alone.
We can also define it as the amount of work (w) needed in order for the body to reach its velocity from a standstill. Mathematical expressions, which quantify how the stored energy in a system depends on its configuration (e.g. Replace “y” and “x” in the general equation with symbols that represent the variables graphed on each axis.
In Classical Mechanics, Kinetic Energy (Ke) Is Equal To Half Of An Object's Mass (1/2*M) Multiplied By The Velocity Squared.
= ½ * 100 * 15 * 15. K=1/2mv² kinetic energy is a scalar quantity; Moment of inertia i of earth = ⅖ * m * r2 = ⅖ * (5.97 × 1024 kg * (6.37 × 106 m)2) = 9.69 * 1037 kg.m2.
It Does Not Have A Direction.
Velocity has more of an impact on an object’s kinetic energy than mass. A 50 kg ball traveling at 20 m/s would have. This means, when th velocity of the object is doubled, its kinetic energy becomes four times.
Comments
Post a Comment